The IRS has announced its 2019 cost-of-living adjustments to tax items that might affect you. Many amounts have increased to account for inflation, but some remain at 2018 levels. As you implement 2018 year-end tax planning strategies, be sure to take into consideration these 2019 adjustments.
Bear in mind that, under the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), annual inflation adjustments are now calculated using the Chained Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (also known as C-CPI-U). The C-CPI-U increases tax bracket thresholds, the standard deduction, certain exemptions, and other figures at a slower rate than the previously used consumer price index, potentially pushing taxpayers into higher tax brackets and making various breaks worth less over time. The law adopts the C-CPI-U on a permanent basis.
Individual income taxes
Tax-bracket thresholds increase for each filing status; but, because they are based on percentages, they increase more significantly for higher brackets. For example, the top of the 10% bracket increases by $175 to $350, depending on filing status, but the top of the 35% bracket increases by $10,300 to $12,350, again depending on filing status.
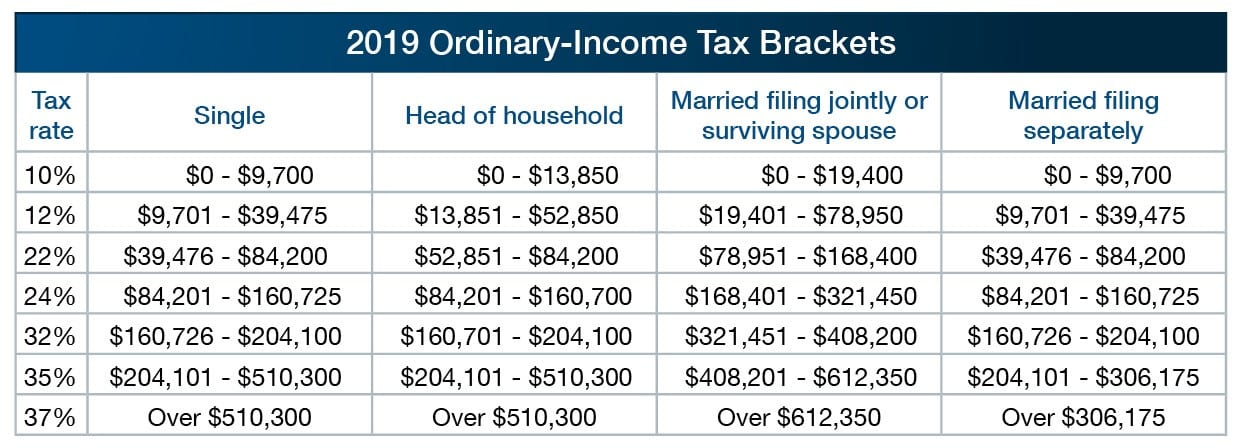
The TCJA suspended personal exemptions through 2025. However, it nearly doubled the standard deduction, indexed annually for inflation through 2025. For 2019, the standard deduction is $24,400 (married couples filing jointly), $18,350 (heads of household), and $12,200 (singles and married couples filing separately). After 2025, standard deduction amounts are scheduled to drop back to the amounts under pre-TCJA law.
Changes to the standard deduction could help some taxpayers make up for the loss of personal exemptions. But it might not help a lot of taxpayers who typically itemize deductions.
Alternative Minimum Tax
The Alternative Minimum Tax (AMT) is a separate tax system that limits some deductions, does not permit others, and treats certain income items differently. If your AMT liability is greater than your regular tax liability, you must pay the AMT.
Like the regular tax brackets, the AMT brackets are annually indexed for inflation. For 2019, the threshold for the 28% bracket increased by $3,700 for all filing statuses except married filing separately, which increased by half that amount.
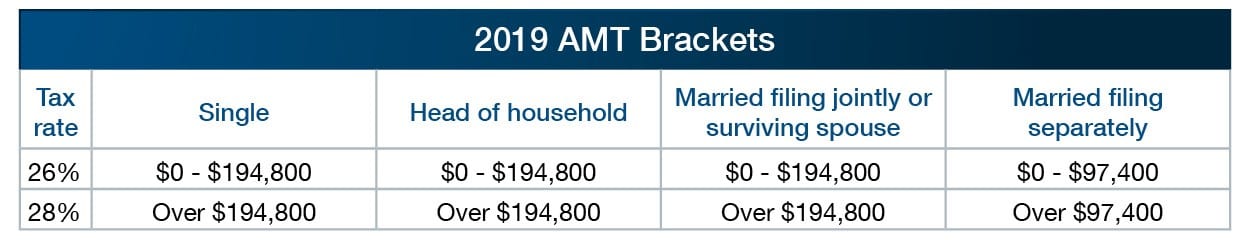
The AMT exemptions and exemption phaseouts are also indexed. The exemption amounts for 2019 are $71,700 for singles and heads of household and $111,700 for joint filers, increasing by $1,400 and $2,300, respectively, over 2018 amounts. The inflation-adjusted phaseout ranges for 2019 are $510,300 – $797,100 (singles and heads of household) and $1,020,600 – $1,467,400 (joint filers). Amounts for separate filers are half of those for joint filers.
Education- and child-related breaks
The maximum benefits of various education- and child-related breaks generally remain the same for 2019. But most of these breaks are limited based on a taxpayer’s modified adjusted gross income (MAGI). Taxpayers whose MAGIs are within the applicable phaseout range are eligible for a partial break—and breaks are eliminated for those whose MAGIs exceed the top of the range.
The MAGI phaseout ranges generally remain the same or increase modestly for 2019, depending on the break. For example:
The American Opportunity Tax Credit. The MAGI phaseout ranges for this education credit (maximum $2,500 per eligible student) remain the same for 2019: $160,000 – $180,000 for joint filers and $80,000 – $90,000 for other filers.
The Lifetime Learning Credit. The MAGI phaseout ranges for this education credit (maximum $2,000 per tax return) increase for 2019. They are $116,000 – $136,000 for joint filers and $58,000 – $68,000 for other filers—up $2,000 for joint filers and $1,000 for others.
The Federal Adoption Tax Credit. The MAGI phaseout ranges for eligible taxpayers adopting a child also increase for 2019—by $4,020 to $211,160 – $251,160 for joint, head-of-household, and single filers. The maximum credit increases by $240, to $14,080 for 2019.
(Note: Married couples filing separately generally are ineligible for these credits.)
These are only some of the education- and child-related breaks that may benefit you. Keep in mind that, if your MAGI is too high for you to qualify for a break for your child’s education, your child might be eligible.
Gift and estate taxes
The unified gift and estate tax exemption and the generation-skipping transfer (GST) tax exemption are both adjusted annually for inflation. For 2019, the amount is $11.40 million (up from $11.18 million for 2018).
The annual gift tax exclusion remains at $15,000 for 2019. It is adjusted only in $1,000 increments, so it typically increases only every few years. It increased to $15,000 in 2018.
Retirement plans
Not all of the retirement-plan-related limits increase for 2019. Thus, you may have limited opportunities to increase your retirement savings if you have already been contributing the maximum allowed amount:
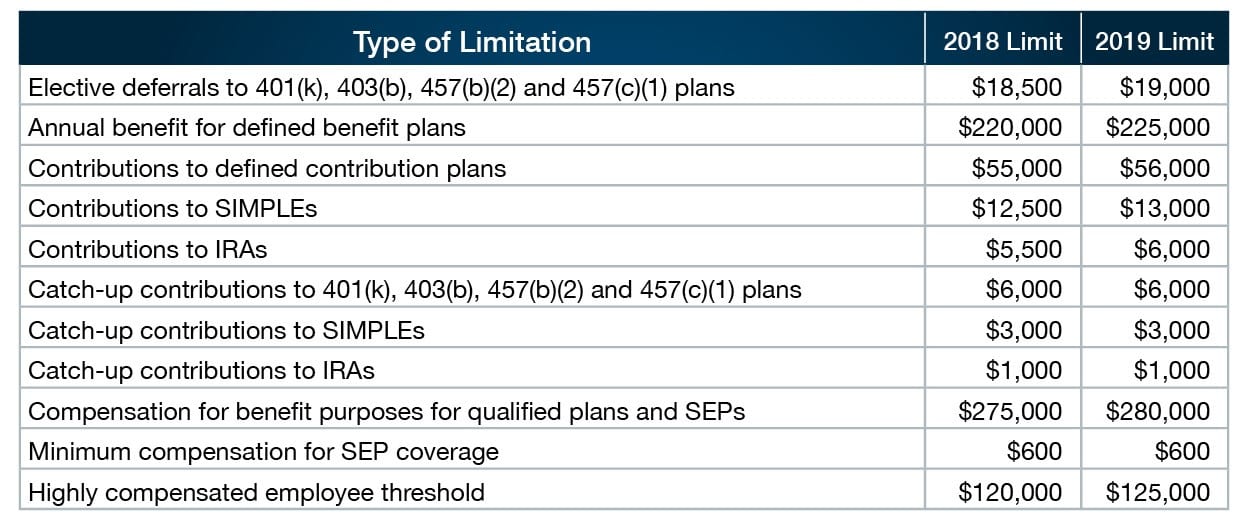
Your MAGI may reduce, or even eliminate, your ability to take advantage of IRAs. Fortunately, all IRA-related MAGI phaseout range limits will increase for 2019:
Traditional IRAs. MAGI phaseout ranges apply to the deductibility of contributions if a taxpayer (or his or her spouse) participates in an employer-sponsored retirement plan:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the phaseout range is specific to each spouse based on whether he or she is a participant in an employer-sponsored plan:
o For a spouse who participates, the 2019 phaseout range limits increase by $2,000, to $103,000 – $123,000.
o For a spouse who does not participate, the 2019 phaseout range limits increase by $4,000, to $193,000 – $203,000.
o For single and head-of-household taxpayers participating in an employer-sponsored plan, the 2019 phaseout range limits increase by $1,000, to $64,000 – $74,000.
Taxpayers with MAGIs within the applicable range can deduct a partial contribution; those with MAGIs exceeding the applicable range cannot deduct any IRA contribution.
But a taxpayer whose deduction is reduced or eliminated can make nondeductible traditional IRA contributions. The $6,000 contribution limit (plus $1,000 catch-up, if applicable, and reduced by any Roth IRA contributions) still applies. Nondeductible traditional IRA contributions may be beneficial if your MAGI is also too high for you to contribute (or fully contribute) to a Roth IRA.
Roth IRAs. Whether you participate in an employer-sponsored plan does not affect your ability to contribute to a Roth IRA, but MAGI limits may reduce or eliminate your ability to contribute:
- For married taxpayers filing jointly, the 2019 phaseout range limits increase by $4,000, to $193,000 – $203,000.
- For single and head-of-household taxpayers, the 2019 phaseout range limits increase by $2,000, to $122,000 – $137,000.
You can make a partial contribution if your MAGI falls within the applicable range, but no contribution if it exceeds the top of the range.
(Note: Married taxpayers filing separately are subject to much lower phaseout ranges for both traditional and Roth IRAs.)
2019 cost-of-living adjustments and tax planning
With the 2019 cost-of-living adjustment amounts trending higher, you have an opportunity to realize some tax relief next year. In addition, with many retirement-plan-related limits also increasing, you have the chance to boost your retirement savings. If you have questions on the best tax-saving strategies to implement based on the 2019 numbers, contact one of our PYA executives below at (800) 270-9629.
© 2018 PYA
No portion of this article may be used or duplicated by any person or entity for any purpose without the express written permission of PYA.


